
This page presents information on the CPUC’s role in addressing the risk of utility-involved wildfires, including critical areas of current and historical regulatory activity and CPUC-reportable fire incident data.Īs the primary regulator of investor-owned electric utilities in California, CPUC must approve the rates utilities charge customers for providing power. The Office of Energy Infrastructure Safety is the primary state agency responsible for reducing the likelihood of utility-involved wildfires. However, fires attributed to power lines consist of roughly half of the most destructive fires in California history.

Historically, utility infrastructure has been responsible for less than 10% of reported wildfires. Other common sources include debris and yard waste burning, motorized equipment and vehicles, campfires, lightning, arson and playing with fire, and smoking. Electric utility infrastructure represents one potential cause of wildfire ignition.

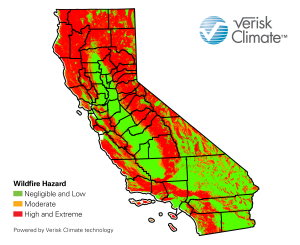
Recent fires have resulted in a devastating loss of life and billions of dollars in property and infrastructure damage. The more extended dry season also increases the chance that the strong offshore winds in the fall coincide with dry conditions, further increasing wildfire risk. The drier fuels also enable fires to spread more rapidly, making them difficult to contain. Hotter, drier conditions during summer and a longer dry season have resulted in lower moisture levels in vegetation, making it easier to ignite. Land use and resource management policies, together with climate change, have increased the likelihood of wildfires starting and the severity of their consequences. In recent decades, the number of fire incidents and acres burned has increased considerably. Wildfire has long been a feature of California’s landscape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
